Training Courses in Concrete Petrography
The training courses focus on the use of optical fluorescence microscopy in quality control, research and forensic analysis of concrete. The training course goes through identification of the individual mineral phases typically present in the concrete, leaching, carbonation, and diagnosis of deterioration processes such as ASR, DEF, sulfate and acid attack, fire damage, F/T damages as well as teaches damages originating in the non-hardened plastic concrete during casting and handling.
The courses address personnel who have basic knowledge of microscopy and mineralogy, have worked with concrete technology and are interested in increasing their knowledge in the field of petrography of concrete.
The courses will typically be held in Taastrup, Denmark, but may also be arranged at your premises. The length of the courses is from 3-5 days.
During the training course you will:
Familiarize with the optical polarizing microscope:
- Ordinary polarized light
- Crossed polarized light without gypsum plate
- Crossed polarized light with gypsum plate
- Fluorescent light



Learn how to:
- Analyze concrete and related materials macroscopically
- Analyze concrete and related materials microscopically by use of optical polarizing microscopy and scanning electron microscopy (SEM)
- Interpret and evaluate petrographic data

Study the concrete microstructure:
- Aggregate; coarse and fine fraction
- Cement type
- Mineral admixtures; FA, MS, slag, fines
- Degree of hydration
- Carbonation & Leaching
- Gel, ettringite, gypsum, calcite, calcium hydroxide…
- Cracking & Corrosion
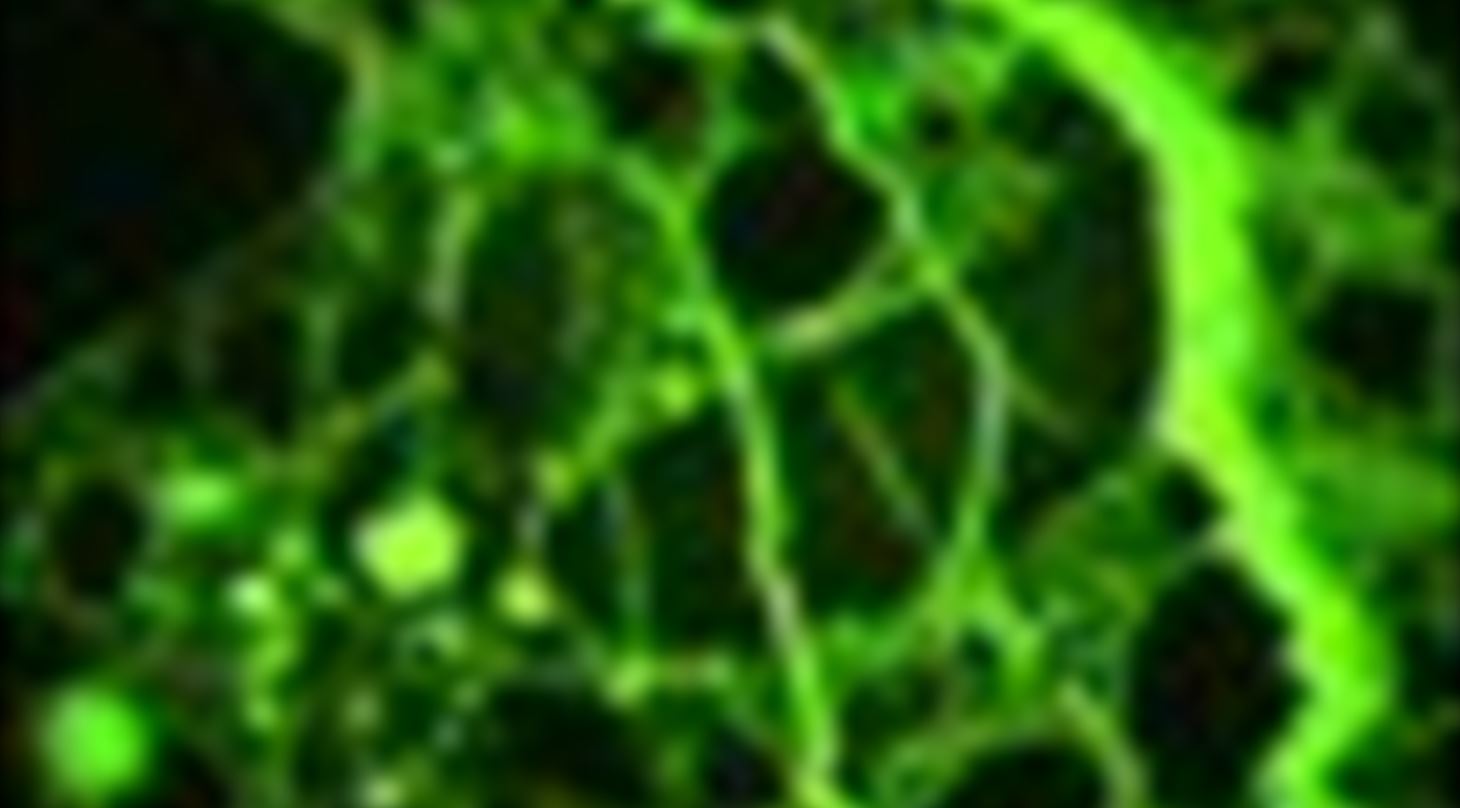
Experience the magic of fluorescence microscopy:
- Determination of the w/c
- Examination of cracks (coarse cracks to cracks less than 10µm's wide)
- Evaluation of paste homogeneity
- Pin point potential ASR aggregates
- Examination of paste defects related to casting (bleeding, cold joints ..)
- Examination of porosity variation in relation to surface treatment
- Examination of air void structure